Sustainability | Formica Group

Materialising Sustainability
The next step in Formica Group’s sustainability journey is a higher level of transparency - proactively communicating our environmental impact data and our plans for improving it in the future.
Formica Group takes a common sense approach to sustainability. This requires the acknowledgment that, by definition, a product requires resources and energy in its creation and as a result, some level of environmental impact will occur. That said, we have adopted the relentless pursuit of maximising our product functionality while minimising its environmental impact. We believe that sustainability is a balancing act between product functionality and its impact. Our goal is to reduce the impacts without losing sight of the product functionality our customers require.
Overall Philosophy
Formica Group’s sustainability policy is built upon a basic motivation to shift from “being less bad” for the environment to being “good” and having a positive impact on the world around us. This approach has three stages:
Do no harm: We will comply with safety, product and sustainability regulations and guidelines set by the countries in which it operates. Beyond that, we will seek opportunities to minimise the environmental impact in all of our operations and products.
Do good: We will support suppliers and customers in realising their sustainability challenges. We will continue to look for opportunities and initiatives to support and promote longer-term sustainability beyond the direct scope of our current operations.
Do better: We believe that investing in sustainability is beneficial to the overall environment and to the long-term health of our business. Many sustainability challenges constitute good business opportunities that support our customers while continuing to allow the company to thrive.
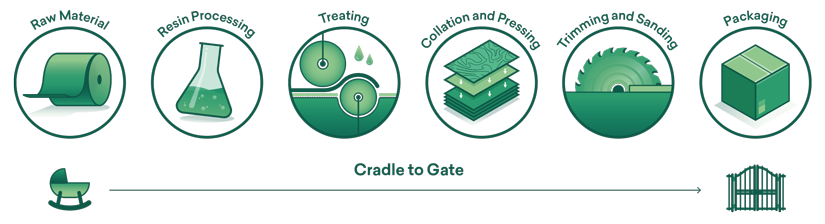
Cradle-to-gate approach
At the heart of Formica Group’s sustainability vision and approach is reducing the impacts generated from the cradle-to-gate portion of our materials life cycle. Our guiding principle is two-fold: increasing efficiency or ”do more with less” and replacing the most impactful energy and material inputs of our process.
Frequently Asked Questions
We use the cradle-to-gate scope for our on-site Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs), because we focus on the stages that are under our control and that we can influence. We are able to improve our processes to make them more efficient and we are continuously working towards using less impactful raw materials. Moreover, for the lifecycle stages that are after our factory gate, we currently don’t have enough data which requires us to make additional assumptions in terms of the disposal of our laminate sheets. Lastly, we are currently waiting on upcoming regulations and a general consensus on the topic of carbon storage benefits of long-lasting products at the end of their lifetime.
Glossary
- Cradle-to-gate: Refers to a partial life cycle assessment where all inputs (raw materials and energy) and outputs (emissions and wastes) are considered from the extraction of raw materials (cradle) to the product is ready to leave the factory (gate). The use and disposal/re-use phases of a product’s life cycle are not taken into account in cradle-to-gate.
- Cradle-to-grave: Refers to the full life cycle assessment, from the extraction of raw materials (cradle) to the transportation, manufacturing, use, and finally disposal or re-use of the product (grave). All inputs (raw materials and energy) and outputs (emissions and wastes) are considered for all the life cycle stages.
Formica® Laminate Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) at formica.info

